Acute Pelvic Pain
Pregnancy
First 5 Minutes
- Rule out pregnancy.
- Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency, though it is frequently missed in the ED.
Context
- Consider the following conditions:
- Gynecological
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Ovarian torsion
- Ovarian cyst
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and Tubo-ovarian abscess
- Endometriosis
- Fibroids
- Gastrointestinal
- Appendicitis
- Diverticulitis
- Urological
- Nephrolithiasis
- UTI (complicated/pyelonephritis)
- Gynecological
Diagnostic Process
- Presentation of common and/or life-threatening gynecological conditions (not exhaustive).
* = potentially life-threatening or surgical emergency.
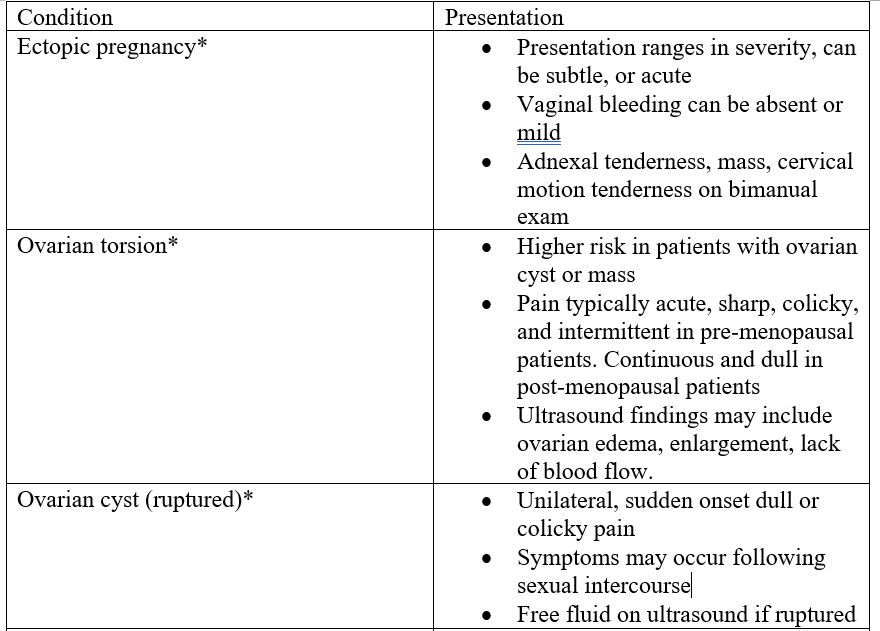

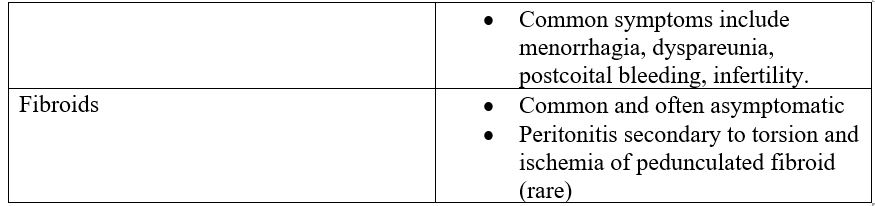
- Assessment
- Thorough gynecological history (LMP, pregnancy history, sexual history, STIs, vaginal bleeding/discharge, etc.).
- Assess for abnormal vitals, perform general abdominal exam, assess for peritonitis.
- Pelvic examination indicated, though is controversial according to some sources.
- Pelvic exam often deferred until ultrasound is acquired if positive Beta-HCG.
- Speculum exam unlikely to change management unless swabs needed for STI testing.
- Bimanual can assess for cervical motion tenderness.
- POCUS
- Can assess for peritoneal free fluid, intrauterine pregnancy, adnexal mass.
- Investigations
- Labs
- Beta-HCG (quantitative)
- CBC, electrolytes, LFTS, creatinine, +/- group and screen
- +/- blood RH factor if pregnant and PV bleeding
- +/- blood culture
- Urinalysis
- STI swabs
- Imaging
- Ultrasound
- Both transabdominal and transvaginal indicated in most cases.
- Indicated to assess for pregnancy location if positive Beta-HCG.
- CT
- Valuable to assess for non-gynecological causes.
- CT abdomen/pelvis for patients with negative Beta-HCG, and clinical signs/symptoms suggestive of gastrointestinal or urological etiologies such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, nephrolithiasis.
- Ultrasound
- Labs
Recommended Treatment
- Symptom management
- Analgesia
- Acetaminophen
- NSAIDs
- Rarely opioids (e.g., hydromorphone 1 – 2 mg PO Q 4-6 hours OR hydromorphone 0.2 – 0.5 mg IV Q 2-4 hours)
- Antiemetics
- Dimenhydrinate PO/IV 25 – 50 mg Q 4-6 hours
- Ondansetron 4 – 8 mg PO/IM/IV Q 4-8 hours
- Antibiotics
- PID
- Mild-moderate (outpatient)
- Doxycycline 100 mg PO Q 24 hours x 14 days AND
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM x1
- +/- metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x 14 days
- Moderate-severe (inpatient)
- Doxycycline 100 mg PO/IV BID
- Cefoxitin 2g IV Q 6 hours
- Mild-moderate (outpatient)
- PID
- Analgesia
Criteria For Hospital Admission
- Diagnosis of a condition requiring surgical management.
- Hemodynamic/vital instability.
Criteria For Transfer To Another Facility
- Transport to facility with surgical capabilities and/or gynecology service may be indicated in unstable patients and/or patients with surgical emergencies.
Criteria For Close Observation And/or Consult
- Abnormal vital signs.
- Evidence of peritonitis on exam.
- Gynecology consult indicated:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Ovarian torsion
- PID
- Tubo-ovarian abscess
- Ovarian cyst (may be appropriate for outpatient management if hemorrhage is minor and no evidence of torsion)
- Malpositioned IUD
- General surgery or urology consult may be indicated for gastrointestinal or urological conditions.
Criteria For Safe Discharge Home
- Patient vitally stable.
- Symptoms manageable with analgesia.
- No evidence of life-threatening or fertility-threatening condition on labs or imaging.
- Outpatient follow-up may be indicated with gynecology (e.g., for dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, ovarian cyst, fibroids).
Quality Of Evidence?

High
We are highly confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. There is a wide range of studies included in the analyses with no major limitations, there is little variation between studies, and the summary estimate has a narrow confidence interval.
Moderate
We consider that the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. There are only a few studies and some have limitations but not major flaws, there are some variations between studies, or the confidence interval of the summary estimate is wide.
Low
When the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. The studies have major flaws, there is important variations between studies, of the confidence interval of the summary estimate is very wide.
Justification
Multiple studies exist regarding pelvic pain, though there is some existing controversy as to the utility of pelvic exams. More resources appear to focus on chronic pelvic pain as opposed to acute pelvic pain.
Related Information
OTHER RELEVANT INFORMATION
Reference List
Brunham RC, Gottlieb SL, Paavonen J. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Campion EW, editor. N Engl J Med. 2015 May 21;372(21):2039–48.
Dewey K, Wittrock C. Acute Pelvic Pain. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 2019 May;37(2):207–18.
Pages-Bouic E, Millet I, Curros-Doyon F, Faget C, Fontaine M, Taourel P. Acute pelvic pain in females in septic and aseptic contexts. Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging. 2015 Oct;96(10):985–95.
Penner RM, Fishman MB. Evaluation of the adult with abdominal pain – UpToDate [Internet]. [cited 2024 Feb 17]. Available from:
Stratton P. Acute pelvic pain in nonpregnant adult females: Evaluation – UpToDate [Internet]. [cited 2023 Dec 9]. Available from:
Relevant Resources
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated Feb 10, 2024
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…


POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.