Concussion – Diagnosis
Neurological, Trauma
Context
- Concussion is synonymous with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI).
- Results from direct external forces to and/or acceleration/deceleration of the head.
- Classic symptoms are confusion and amnesia, with or without loss of consciousness.
mTBI Definition (World Health Organization)
1. One or more of:
- confusion or disorientation
- loss of consciousness ≤ 30 minutes
- post-traumatic amnesia ≤ 24 hours
- other abnormalities such as focal signs, seizure, and intracranial lesions not requiring surgery.
2. Glasgow Coma Scale score of 13-15 ≥ thirty minutes post-injury.
3. Not due to:
- drugs, alcohol, or medications
- other injuries or their treatments (e.g. systemic injuries, facial injuries or intubation)
- psychological trauma, communication barrier or coexisting medical conditions
- penetrating injury.
Diagnostic Process
- MRI is generally not indicated
Head CT based on the Canadian CT Head Rule
- High-Risk Injury (may require neurosurgical intervention)
- GCS score < 15 at 2 hr after injury
- Suspected open or depressed skull fracture
- Signs of basal skull fracture (hemotympanum, periorbital bruising (Raccoon eyes), CSF otorrhea or rhinorrhea, retroauricular bruising (Battle’s sign))
- Vomiting ≥ two episodes
- Age ≥ 65 years.
- Medium-Risk Injury (may have important brain injury on CT)
- Amnesia before impact ≥ 30 min
- Dangerous mechanism (pedestrian struck by vehicle, occupant ejected from vehicle, fall from elevation >3 feet [five stairs]).
- Rule not applicable if:
- Non-trauma cases
- GCS < 13
- Age < 16
- Coumadin or bleeding disorder.
- Obvious open skull fracture
- Additionally, others recommend CT if:
- Neurologic deficits
- Seizure
- Bleeding diathesis or oral anticoagulant use
- Return visit for reassessment of a head injury.
Clinical diagnosis of concussion
Common symptoms of mTBI are diffuse and variable:
- Headache
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Fatigue
- Drowsiness
- Visual changes (ie. diplopia, or blurry vision, photophobia)
- Insomnia or hypersomnia
- Difficulty multitasking, attentional dysfunction, short-term memory and learning problems
- Phonophobia
- Emotional changes.
Common signs of mTBI:
- Loss of consciousness
- Anterograde or retrograde amnesia
- Confusion
- Emotional lability
- Behaviour or personality changes.
Criteria For Hospital Admission
- GCS <15
- CT head abnormalities
- Seizures
- Underlying bleeding diathesis or oral anticoagulation
- Neurologic deficit
- Recurrent vomiting.
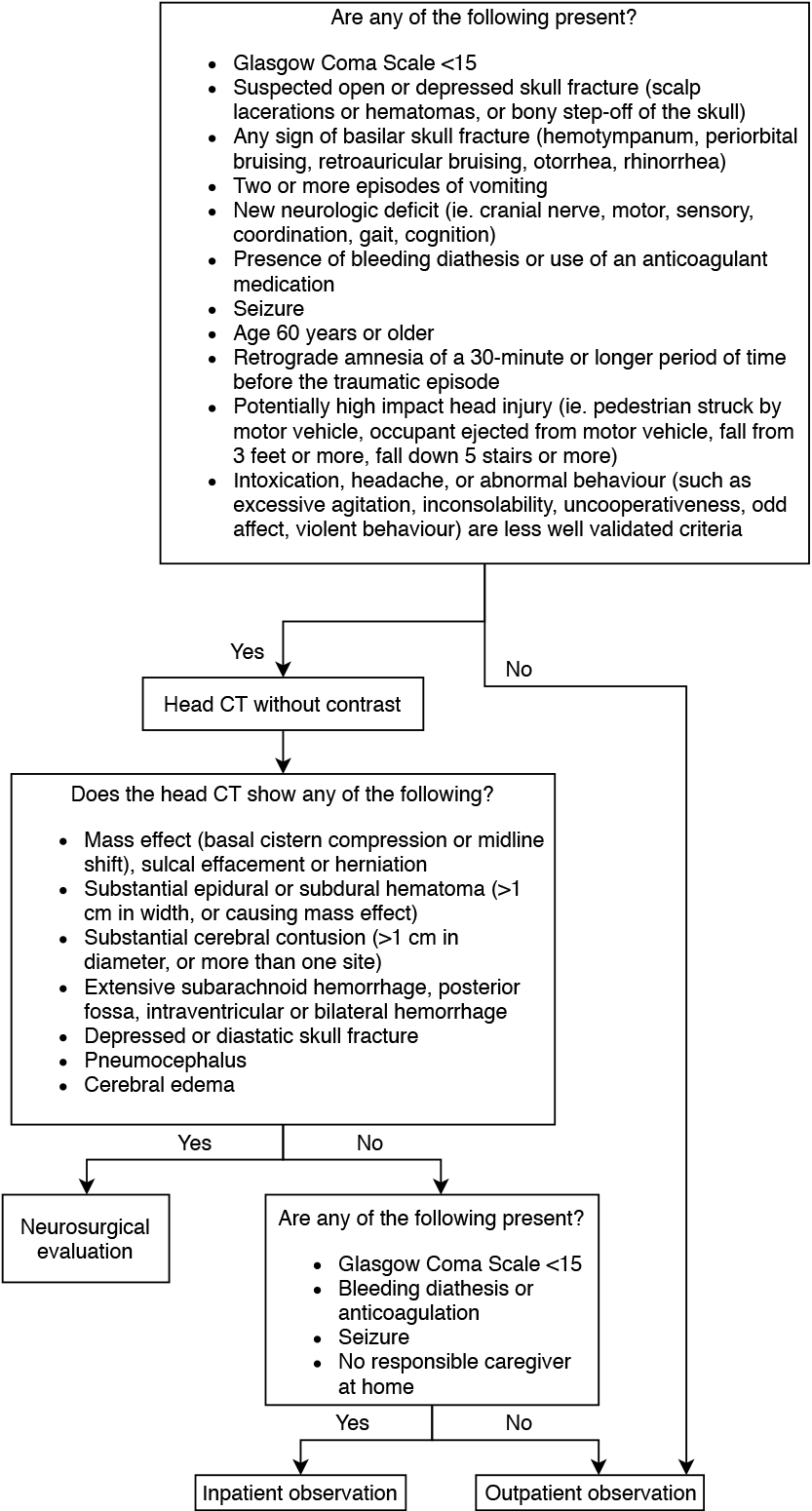
Acute evaluation of an adult with mild head trauma:
CLICK TO ENLARGE
Adapted from UpToDate: Acute mild traumatic brain injury (concussion) in adults
Related Information
Reference List
Relevant Resources
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated Aug 07, 2019
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…


POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.