Pediatric Blood Transfusion
Cardiovascular, Hematological / Oncological
Context
Does not apply to neonatal transfusions, which for the purpose of transfusion medicine, is an infant under 4 months of age.
The most commonly transfused pediatric patients are those in PICU, those undergoing cardiac surgery, transfusion-dependent children with inherited conditions, and those following intensive chemotherapy.
Red Blood Cells
- The two major indications for RBC transfusions are prevention or alleviation of symptoms, and signs of inadequate oxygen delivery.
- When deciding to transfuse a critically ill pediatric patient, the overall clinical context must be taken into account.
- As in adults, critically ill children benefit from a restrictive transfusion strategy (70 g/L).
- RBC transfusion is often recommended in critically ill children or those at risk for critical illness when the hemoglobin concentration is <50 g/L. Transfusion is not recommended in hemodynamically stable patients with a hemoglobin concentration 70 g/L.
- Clinical judgment is required for hemoglobin between 50 – 70 g/L.
- RBC transfusions are dosed at 10ml/kg.
- In hemorrhagic shock, RBCs, plasma, and platelets should be transfused in a ratio of 2:1:1 or 1:1:1.
- Acute brain injuries, consider RBC transfusion if hemoglobin is 70-100 g/L.
- Oncologic diagnoses, or those undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant, consider RBC transfusion if hemoglobin 70-80 g/L.
- Uncorrected congenital heart disease, maintain hemoglobin of 70-90 g/L depending on cardiac reserve.
Platelets and Plasma
- In general, guidelines for adult patients are applied to children due to the lack of high-grade evidence.
- Platelet transfusions are indicated to prevent or decrease bleeding in the context of quantitative or qualitative platelet disorders.
- Dose platelets are typically 5 to 10 mL/kg.
- The main indication for plasma transfusion is the correction of bleeding from multiple acquired coagulation factor deficiencies.
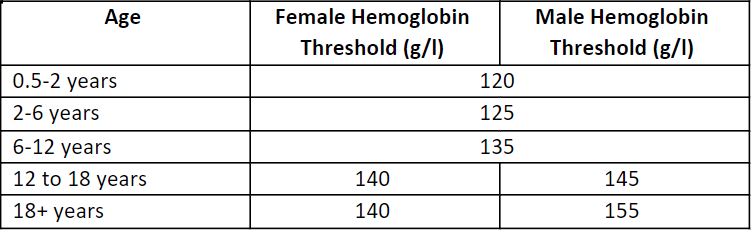
Normal hemoglobin values (Lau, 2017).
Created by Ella Barrett-Chan, MSI UBC 2023
Indications for transfusion of red blood cells (Lau, 2017).
Indications for transfusion of plasma (Lau, 2017)
Quality Of Evidence?

High
We are highly confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. There is a wide range of studies included in the analyses with no major limitations, there is little variation between studies, and the summary estimate has a narrow confidence interval.
Moderate
We consider that the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. There are only a few studies and some have limitations but not major flaws, there are some variations between studies, or the confidence interval of the summary estimate is wide.
Low
When the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. The studies have major flaws, there is important variations between studies, of the confidence interval of the summary estimate is very wide.
Justification
Moderate. Based on clinical guidelines.
Related Information
Reference List
Neonatal and pediatric transfusion. Professional Education. Chapter 13
Lau, W. (2017, August 2).
Canadian Blood Services
-
Consensus Recommendations for RBC Transfusion Practice in Critically Ill Children From the Pediatric Critical Care Transfusion and Anemia Expertise Initiative.
Valentine, S. L., Bembea, M. M., Muszynski, J. A., et. al. 19(9), 884–898.
– Pediatric Critical Care Blood Research Network (BloodNet), and the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury and Sepsis Investigators (PALISI) Network (2018). Pediatric critical care medicine: a journal of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the World Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care Societies.
Relevant Resources
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated Sep 08, 2021
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…




POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.