Elbow Fractures
Orthopedic, Trauma
First 5 Minutes
- Assess the neurovascular status of the injured extremity. Check for changes in sensation, motor function and pulses distal to the fracture site.
- Look for evidence of obvious deformities or compound fracture.
Context

Figure 1 (Left): Anterior view of the elbow joint. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:202107_Anterior_view_of_the_elbow_joint.svg. Image adapted from Wikimedia Commons. Figure 2 (Right): Posterior view of the elbow joint. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:202107_Posterior_view_of_the_elbow_joint.svg. Image adapted from Wikimedia Commons.
- The elbow is a synovial hinge joint that connects the humerus to the ulna and radius, and is stabilized by 4 major ligaments.
Diagnostic Process
- Conduct a complete neurovascular examination of the injured extremity.
- Assess for open fracture.
- Examine the joint above and below the suspected area of injury as pain can radiate.
- Integrity of the supporting ligaments may be tested via the varus and valgus stress tests, however, limiting movement is recommended if fracture is suspected.
Imaging:
- The elbow extension test can be used to guide the decision to order radiography — patients who can fully extend their elbow have a low chance of fracture.
Types of fractures commonly seen:
- Radial head fracture.
- Olecranon fracture.
- Coronoid fracture.
- Monteggia fracture-dislocation (uncommon but often mentioned).
Recommended Treatment
Orthopedic referral is recommended for all but radial head fractures that do not impair supination/pronation.
Non-operative Management:
- Conservative management is indicated for non-displaced fractures.
- Most patients will recover via immobilization by a cast or splint.
- Long arm cast: Used for severe or unstable elbow fractures that require rigid immobilization.
-
- Long arm posterior splint:
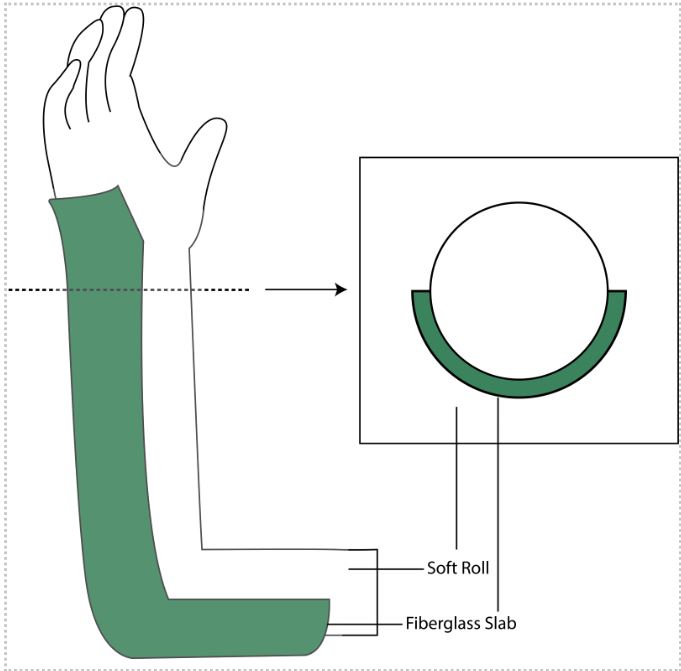
Created by Ella Barrett-Chan, MSI UBC 2023
Criteria For Hospital Admission
Hospital admission should be considered for patients with:
- Open, displaced or complex fractures, or
- Vascular or neurological compromise.
Criteria For Transfer To Another Facility
Consider transferring patients to another facility if:
- The patient has a severe elbow fracture that requires specialized care that is not available at the current facility.
Quality Of Evidence?

High
We are highly confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. There is a wide range of studies included in the analyses with no major limitations, there is little variation between studies, and the summary estimate has a narrow confidence interval.
Moderate
We consider that the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. There are only a few studies and some have limitations but not major flaws, there are some variations between studies, or the confidence interval of the summary estimate is wide.
Low
When the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. The studies have major flaws, there is important variations between studies, of the confidence interval of the summary estimate is very wide.
Justification
Related Information
Reference List
Boyd AS, Benjamin HJ, Asplund C. Splints and Casts: Indications and Methods. afp. 2009 Sep 1;80(5):491–9.
Walthall J, Adame JD, Varacallo M. Long Arm Splinting. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2023 May 19]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513283/
Appelboam A, Reuben AD, Benger JR, Beech F, Dutson J, Haig S, et al. Elbow extension test to rule out elbow fracture: multicentre, prospective validation and observational study of diagnostic accuracy in adults and children. BMJ. 2008 Dec 9;337:a2428.
Goldflam K. Evaluation and Treatment of the Elbow and Forearm Injuries in the Emergency Department. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 2015 May 1;33(2):409–21.
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated Jun 17, 2023
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…


POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.