Peri-Arrest in Pregnancy: Diagnosis and Management
Cardiovascular, Critical Care / Resuscitation
Context
- Incidence of cardiac arrest during pregnancy in Canada: 1:12,500 deliveries.1
- Potential Contributing Factors (A-H)
- Anesthetic complications: high neuraxial block, loss of airway, aspiration, respiratory depression, hypotension, local anesthetic systemic toxicity.
- Bleeding: coagulopathy, uterine atony, placenta accreta, placental abruption, placenta previa, uterine rupture, trauma, surgical, transfusion reaction.
- Cardiovascular: cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, aortic dissection, arrhythmias.
- Drugs: anaphylaxis, overdose, error, magnesium, opioid, insulin, or oxytocin.
- Embolic: pulmonary embolus, amniotic fluid, air.
- Fever: sepsis.
- General: non-obstetric causes of cardiac arrest.
- Hypertension: preeclampsia/eclampsia/HELLP, intracranial bleed.
Diagnostic Process
Investigations based on potential etiology2:
- Note: Use table as an adjunct to the AHA Guidelines when exploring causes of the peri-arrest.
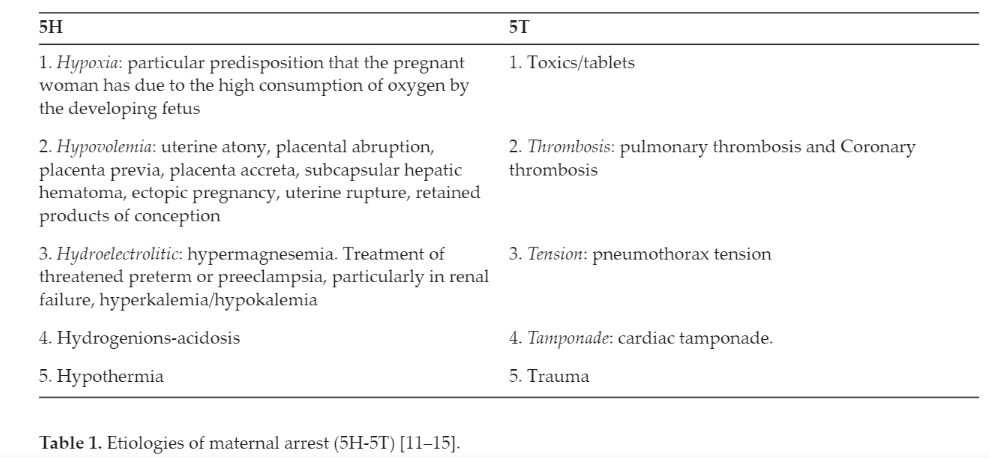
Diagnostic process Table 1. Etiologies of maternal arrest (5H-5T) page 3
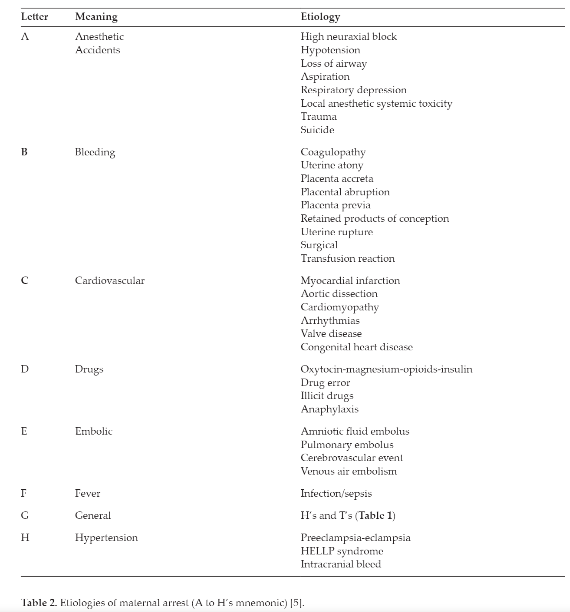
Table 2. Etiologies of maternal arrest (A to H’s mnemonic) page 4
Recommended Treatment
Treatment algorithm is based on the 2020 AHA Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care3:
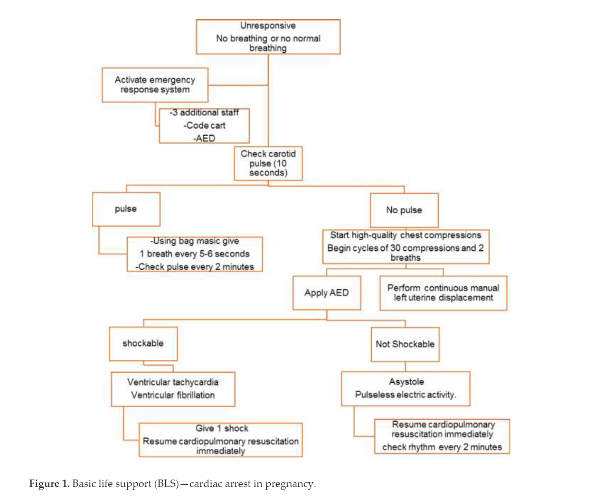
Management (Figure 1. Basic life support (BLS)-cardia arrest in pregnancy.) page 6
Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care CPR in pregnancy
- Women who remain comatose after resuscitation.
- Targeted temperature management for pregnant patient is recommended and fetus should be continuously monitored for bradycardia.
Quality Of Evidence?

High
We are highly confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. There is a wide range of studies included in the analyses with no major limitations, there is little variation between studies, and the summary estimate has a narrow confidence interval.
Moderate
We consider that the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. There are only a few studies and some have limitations but not major flaws, there are some variations between studies, or the confidence interval of the summary estimate is wide.
Low
When the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. The studies have major flaws, there is important variations between studies, of the confidence interval of the summary estimate is very wide.
Justification
The treatment algorithm is based on the 2020 AHA Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Recommendations were based on expert opinion and limited data (observational or registry studies with limitations in design and execution, meta-analyses of such studies, and physiological or mechanistic studies).
Related Information
Reference List
Balki M, Liu S, León JA, Baghirzada L. Epidemiology of Cardiac Arrest During Hospitalization for Delivery in Canada: A Nationwide Study. Anesth Analg. 2017;124(3):890-897.
Helviz Y, Einav S. Maternal cardiac arrest. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019;32(3):298-306.
Panchal AR, Bartos JA, Cabañas JG, et al. Part 3: Adult Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2020;142(16_suppl_2):S366-S468.
RESOURCE AUTHOR(S)

DISCLAIMER
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by Emergency Care BC (formerly the BC Emergency Medicine Network) and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. Emergency Care BC is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. Emergency Care BC also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
Last Updated May 10, 2022
Visit our website at https://emergencycarebc.ca
COMMENTS (0)
Add public comment…


POST COMMENT
We welcome your contribution! If you are a member, log in here. If not, you can still submit a comment but we just need some information.